Dexamethasone Injection for Dogs: How Long Does It Last?
Dexamethasone is a steroid drug that can be administered intravenously to dogs to treat a variety of ailments, including inflammation, allergic responses, and specific malignancies. The particular dog, the dose given, and the ailment being treated can all affect how long its effects last.
Dexamethasone injectable side effects typically last from a few hours to a few days. The effects can last longer if the medicine is administered in a series of injections over a few days or weeks.
How Long Does Dexamethasone Last in Dogs?
It is given to dogs as an injection that treats several ailments, such as allergic reactions, inflammation, and certain kinds of cancer. The duration of the effects of dexamethasone will vary based on a variety of variables, including the dose given and the dog’s age, as well as the problem being treated.
The Half-Life of Dexamethasone in Dogs
The half-life of medicine is the amount of time it takes for half of the dose given to be eliminated from the body. The half-life of dexamethasone in dogs is around 3 hours. It means that, after three hours, the majority of the dose will be taken out of the dog’s system. In the next 3 hours, a quarter of the remaining dose is eliminated, and the cycle continues. So the effects of just one dose of dexamethasone can last several hours.
The duration of the effects of dexamethasone in dogs may also depend on the dose given and the frequency at which it is administered. If a dog receives high doses of dexamethasone, the effects could last longer than those of those who received a lower dose. In the same way, when a dog is given many doses of dexamethasone, the effects could be longer-lasting than if they received only one dose.
If the dog receives dexamethasone as a treatment for an ongoing condition like cancer, the vet will give the drug in an infusion series over some time, such as weeks or days. In this situation, the dexamethasone effects could be longer-lasting than if the dog was given only one injection.
The Dog’s Age and Health Status
The health and age of a dog may influence the duration of the effects of dexamethasone. As a rule, older dogs tend to process medications slower than younger dogs. This may result in more lasting effects. Furthermore, dogs suffering from chronic health issues like kidney or liver disease might be unable to remove medications from their bodies in the same way, which could cause longer-lasting effects.
The duration of the effects of dexamethasone will also depend on the disease being treated. For instance, when a dog receives dexamethasone to treat an acute allergic reaction, the results could be brief, lasting only several hours. However, in the case of receiving dexamethasone to treat a chronic illness like arthritis or cancer, the effects could last for a longer time.
It is important to remember that although dexamethasone can help with symptoms, it cannot treat the root cause of the problem. Therefore, following your veterinarian’s advice carefully and reporting any changes or concerns you experience while your dog is being treated is essential.
What Happens When Dexamethasone Wears Off?
Dexamethasone is one of the most commonly used medications for steroid use in veterinary medicine. It is administered to dogs for injections that treat various ailments, such as allergic reactions, inflammation, and some types of cancer. While dexamethasone can help alleviate symptoms, it is important to know what happens after its effects fade.
Return of Symptoms
One of the most important effects of dexamethasone’s wear-off in dogs is the recurrence of symptoms. Dexamethasone, a medicine, offers relief from pain, inflammation, and other symptoms that are associated with various ailments. However, after the medication is gone, symptoms can recur. This is particularly problematic when a chronic condition is present, such as cancer or arthritis in dogs, which might require ongoing treatment to control their symptoms.
As well as the recurrence of symptoms, the wear-off of dexamethasone can cause increased discomfort and pain for dogs. Dexamethasone can help relieve discomfort and pain caused by inflammation, but when its effects cease, the discomfort and pain can return. This is especially true for dogs suffering from arthritis, where pain management is a crucial component of treatment.
Risk of Side Effects
Another consequence of dexamethasone wearing off in dogs is possible adverse effects. Dexamethasone is a powerful medication that may cause serious negative effects, especially when given in high doses or over prolonged periods. When the medication stops working, the risk of adverse effects will diminish. However, should the dog require continual treatment with dexamethasone, the chance of experiencing side effects can increase over time.
When the dexamethasone effects wear off, offering additional treatment to the dog is possible. This could include more injections of dexamethasone or other medications to treat the symptoms that dogs experience. For instance, when a dog suffering from arthritis receives dexamethasone injections to reduce the pain they experience, it might also require other pain medications to treat its symptoms after the dexamethasone is gone.
Risks and Side Effects of Dexamethasone Injection in Dogs
Dexamethasone is a powerful steroid medication employed to treat various conditions in dogs, such as allergic reactions, inflammation, and certain types of cancer. While it is an effective treatment alternative, there are dangers and adverse effects associated with dexamethasone injections in dogs.
Increased Appetite and Weight Gain
One of the common side effects of dexamethasone in dogs is a rise in appetite and weight gain. This can be a problem for dogs who are already obese or have an unhealthy history. Dexamethasone can cause dogs to consume more food than normal, increasing calories consumed and weight gain. Sometimes, it can cause a recurrence of existing health issues like diabetes or arthritis.
Along with weight gain, dexamethasone may also alter your body composition. Steroid medications such as dexamethasone could cause muscle loss and weight gain, despite a small growth in body fat. This is a problem for dogs who require muscle mass to help with mobility and other purposes.
Increased Thirst and Urination
Another possible side effect of dexamethasone injections in dogs is increased thirst and urine production. Dexamethasone could cause dogs to drink more water than they normally do, increasing their desire to go to the bathroom.
This can be a problem when the dog is incapable of holding the urine for prolonged periods or when they are susceptible to urinary tract infections. The increased thirst and urination could be an indication of more serious negative side effects, such as diabetes or kidney damage.
If your dog has an increase in thirst and urination following dexamethasone, it is vital to keep track of the amount of water they drink and the frequency of their urination. If you observe any changes or have any concerns, consult your veterinarian.
Weakened Immune System
One of the major risks associated with dexamethasone injections for dogs is weakening the immune system. Dexamethasone acts as an immunosuppressant, which means it will inhibit a dog’s immune system.
While this may be beneficial in certain circumstances, such as managing autoimmune diseases, it also leaves the dog at risk of illnesses and other health issues. In certain instances, prolonged use of dexamethasone may increase the likelihood of developing health issues.
It is crucial to follow your veterinarian’s instructions when administering dexamethasone treatment to your dog, especially in the case of a history of infections or other health issues related to the immune system. Your veterinarian may suggest additional monitoring or medications to help support your pet’s immune system when they receive dexamethasone.
Dexamethasone injections in dogs can cause gastrointestinal issues, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and vomiting. These adverse effects can be particularly troublesome for dogs with pre-existing digestive issues like pancreatitis or inflammatory bowel diseases. In the most severe instances, digestive issues caused by dexamethasone may result in electrolyte imbalances, dehydration, and other health problems.
If your dog has stomach-related side effects after receiving dexamethasone, it is essential to monitor the symptoms and consult your veterinarian if you are concerned. Your veterinarian may suggest diet or medication adjustments to help manage the symptoms and prevent complications.
How to Care for a Dog After Dexamethasone Injection?
Dexamethasone injections can effectively treat various dog ailments, such as allergic reactions, inflammation, and certain kinds of cancer. After receiving dexamethasone, it is crucial to provide proper treatment and follow-up to maintain the health and well-being of your dog.
Monitor for Side Effects
The most crucial aspect of caring for dogs after a dexamethasone injection is monitoring for possible adverse effects. Dexamethasone may cause various adverse effects, including increased thirst and appetite, behavioral changes, stomach issues, and a weakening immune system. It is crucial to be aware of possible side effects and to monitor your dog to detect any change in behavior, appetite, or health.
If you notice any alarming symptoms, like diarrhea, vomiting, increased thirst, or urination, consult your veterinarian. Your veterinarian might recommend further monitoring or medications to control these effects and ensure your dog’s comfort.
After receiving dexamethasone, the dog might be afflicted with fatigue or lethargy. Providing sufficient rest and a calm and quiet space for the dog to recuperate is essential. Limit vigorous activities like running or jumping, and avoid stressing the dog or excessively stimulating situations.
If your dog is suffering from discomfort or pain, your veterinarian may suggest using pain medications or other ways to treat the symptoms. Ensure you follow your veterinarian’s instructions for medication administration and dosage.
Maintain a Healthy Diet
Dexamethasone may increase appetite and result in weight gain, so it is crucial to ensure a healthy diet for your dog following the injection. Avoid feeding the dog too much or giving them excessive treats or snacks. Instead, concentrate on providing a balanced and healthy diet appropriate for the dog’s needs.
Your veterinarian may suggest diet adjustments or supplements to help support your dog’s recovery and health. Make sure you adhere to the advice of your veterinarian and keep track of your dog’s body weight and general health regularly.
Ultimately, it is crucial to keep in touch with your veterinarian after the dog receives a dexamethasone shot. Your veterinarian will be able to monitor your dog’s health and its improvement and suggest any follow-up treatment or monitoring.
Based on the reason for the dexamethasone injection, your veterinarian may suggest additional tests or treatments to treat the dog’s root disease. Follow your veterinarian’s instructions carefully and address any concerns or questions you may have about the dog’s health or recovery.
In the end, caring for dogs after dexamethasone injections requires attentive monitoring, rest, a balanced diet, and regular check-ups with your vet. With proper treatment and care, dogs can recover from dexamethasone shots and enjoy better health and ease.
How To Administer Dexamethasone Injection At Home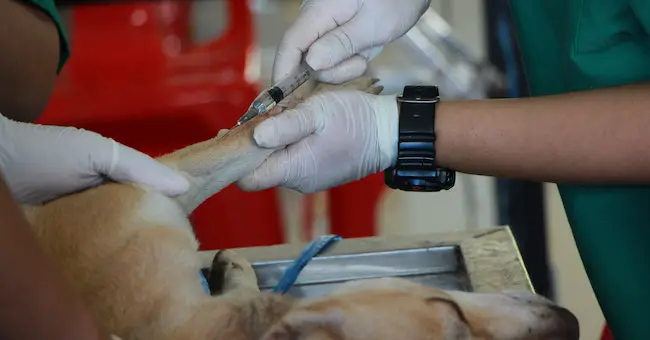
Giving dexamethasone injections at home is an effective treatment for certain dog ailments; however, following the correct procedures is essential to ensuring your dog’s safety and security.
Before administering a dexamethasone injection at home, it’s crucial to consult your veterinarian. Your veterinarian can decide whether home administration is suitable for your dog’s health and will provide specific instructions and guidelines for dosing.
Your doctor may also suggest additional training or assistance to ensure you’re comfortable and confident when giving the injection. Make sure to inquire about any concerns and follow your physician’s instructions carefully.
Gather Supplies
To administer dexamethasone injections at home, you’ll need the proper equipment. They could include:
- Dexamethasone injection vial
- Syringe and needle
- Alcohol wipes
- Gloves
- Sharps container to dispose of needles and syringes
Ensure you have all the necessary items before giving the injection, and then store them in a secure place.
Prepare the Injection
Before injecting, it is crucial to get the injection area and the injection. Start by cleaning the injection area with alcohol wipes and letting it dry completely. Then remove the cap of the dexamethasone injection vial and inject the correct dose into the syringe.
Ensure you follow your physician’s directions carefully regarding dosage and administration techniques. It might be beneficial to practice drawing the injection using water or sterile saline before giving the actual drug.
Administer the injection
To inject the medication, hold the syringe as if holding a pencil and place the needle inside the clean injection site at a 90-degree angle. Slowly press the plunger to inject medication, then take the needle out of the injection site and discard it into a sharps container.
When administering the injection, wash the area with an alcohol wipe. Then keep an eye on the dog for any indications of discomfort or adverse reactions. Contact your veterinarian if you have any questions or concerns regarding the injection.
In conclusion, giving dexamethasone at home is beneficial for some dog issues. However, it is crucial to speak with your vet. Collect the necessary equipment, safely make the injection, and administer the shot properly and safely. With the proper instruction and direction, you are able to offer safe and effective treatment for your pet at home.
How to Store Dexamethasone Injection for Dogs
Proper storage of dexamethasone injections for dogs is vital to ensuring their effectiveness and security.
Follow the Manufacturer’s Instructions
The first step in storing dexamethasone for dogs is following the manufacturer’s instructions. These instructions can differ based on the particular dosage and product. Be sure to follow all directions included with your medication.
The manufacturer’s instructions could include specific information about the right storage temperature, the recommended storage duration, and any additional precautions to be taken when storing the medication.
Store in a Cool, Dry Place
Dexamethasone injections are best stored in a cool, dry location to preserve their effectiveness and potency. The ideal temperature for storage can differ based on the specific product; however, an average temperature of 20–25 °C (68–77 °F) is generally recommended.
Avoid placing the medication in areas exposed to intense heat, direct sunlight, or humidity. These conditions could cause the medication to decrease in effectiveness faster and decrease its effectiveness.
Be Safe From Light
Dexamethasone injections should be shielded from sunlight to preserve their effectiveness. Exposure to light can cause the drug to break down more quickly and reduce its effectiveness.
Place the medication in an opaque container or protect the medication from sunlight exposure. If your medication comes in a clear container, you should consider keeping it in a dark, closed space like an open cabinet or drawer.
Properly Dispose of Expired Medication
It is essential to regularly check the expiration date for dexamethasone injections and dispose of any expired medication. Expired medications could not be as effective or safe to use.
Consult your doctor or local pharmacy to find the most appropriate way to dispose of expired medications. Do not dispose of any medication in your garbage bin or flush it into the toilet, as this could harm other animals and the environment.
In short, proper storage of dexamethasone for dogs means following the directions of the manufacturer, storing the medication in a dry, cool area, securing it from the sun, and getting rid of expired medications. Follow these guidelines to ensure the effectiveness of the medication as well as security in the treatment of your dog.
FAQ’s
What is Dexamethasone injection for dogs?
Dexamethasone injection is a corticosteroid medication commonly used to treat inflammation and various diseases in dogs.
How is Dexamethasone injection administered to dogs?
Dexamethasone injection is administered intravenously, intramuscularly, or subcutaneously by a veterinarian.
How long does Dexamethasone injection last in dogs?
The duration of Dexamethasone injection’s effect in dogs depends on the dose, severity of the condition, and the individual dog’s response. Generally, the effects can last from 12 to 36 hours.
What are the side effects of Dexamethasone injection in dogs?
The potential side effects of Dexamethasone injection in dogs include increased thirst and urination, increased appetite, panting, restlessness, lethargy, gastrointestinal upset, and behavioral changes.
Can Dexamethasone injection be used long-term in dogs?
Long-term use of Dexamethasone injection in dogs is not recommended because it can cause significant side effects such as adrenal suppression and immunosuppression.
When should I contact a veterinarian if my dog receives Dexamethasone injection?
You should contact a veterinarian immediately if you notice any concerning side effects or if your dog’s condition does not improve after receiving Dexamethasone injection. It is essential to follow the veterinarian’s.


















